Affiliation between oral hygiene information and practices amongst older dental sufferers attending non-public dental clinics in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
A facility-based cross-sectional study was conducted at the Nash Specialty Dental Clinic, Sitamin Medium Dental Clinic, Dent-Efrata Dental Clinic, and Merit Medium Dental Clinic in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. All are located in Addis Ababa, the capital of Ethiopia. The choice of clinics rather than hospitals is likely a trade-off between practicality and availability of resources, as clinics cover a wider range of patients suitable for the study. Clinics were selected based on patient flow. By focusing on private dental clinics, the research team was able to efficiently access the target population of older dental patients and collect the necessary data to examine the association between oral hygiene knowledge and practices. The data were collected between November 17, 2022, and December 18, 2022.
The source population was older dental patients treated in private dental clinics in Addis Ababa. The study population consisted of older dental patients receiving treatment in private dental clinics during the data collection period. Dental patients who were 65 years or older were included in the study, whereas older dental patients who were unable to communicate due to their health condition were excluded.
A convenience sampling method was used to select study participants. The sample size was calculated using a formula for the proportion of a single population, considering the following assumptions: p = 32%, the prevalence of oral hygiene knowledge [10], a confidence level of 95%, and a margin of error of 5%. The initial sample size was less than 10,000 people, and a finite population correction formula was used to calculate the optimal sample size. The final sample size was 111 study participants.
$${{{{{\rm{n}}}}}} ={{{{{\rm{Z}}}}}}{{{{{\rm{\alpha }}}}}}/{{2}^{2}} \, {}^{\ast }{{{{{\rm{p}}}}}} {}^{\ast} (1-{{{{{\rm{p}}}}}})/{{{{{\rm{d}}}}}}2\\ ={(1.96)}^{2}(0.32)(1-0.32)/{(0.05)}^{2}$$
$${{{{{\rm{n}}}}}}=334({{{{{\rm{calculated}}}}}}\; {{{{{\rm{sample}}}}}}\; {{{{{\rm{size}}}}}})+33.4(10 \% {{{{{\rm{nonresponse}}}}}}\; {{{{{\rm{rate}}}}}})$$
$${{{{{\bf{n}}}}}}={{{{{\bf{367}}}}}}$$
Since the total population was 160, the population correction formula was used to correct the size of the sample;
$${{{{{\rm{Correction}}}}}}\; {{{{{\rm{formula}}}}}}={{{{{\bf{n}}}}}}/({{{{{\bf{1}}}}}}+{{{{{\bf{n}}}}}}/{{{{{\bf{N}}}}}})\\ =367/(1+367/160)\\ ={{{{{\mathbf{111}}}}}}({{{{{\mathbf{sample}}}}}}\; {{{{{\mathbf{size}}}}}})$$
A structured questionnaire was developed based on a review of the literature. The data collection instrument included three parts: questions that evaluated sociodemographic characteristics, questions about the participant’s level of knowledge about oral hygiene, and questions about oral hygiene practices. The questionnaire was prepared in English, translated into Amharic, and back-translated to English to confirm its accuracy. The questionnaire was pretested in 5% of older dental patients attending an unselected dental clinic to test its feasibility and clarity. The questionnaire was revised and refined to improve its validity and reliability based on the pretest results. Moreover, the content and face validity of the questionnaire were measured based on the experts’ judgments.
Data collectors and supervisors were trained on the purpose of the study, questionnaire administration, and data collection procedures. An interviewer’s structured Amharic version of the questionnaire was used for data collection. Four nurses collected the data, and four dental specialists supervised the data collection procedure. The completeness and consistency of the data were checked. The coded data were entered, cleaned, and analyzed using SPSS version 23 software. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the data. Logistic regression was applied to measure the association between oral hygiene knowledge and oral hygiene practices. Multiple logistic regression was used to identify associated factors. Statistical significance was assessed at the 0.05 level. In the bivariate analysis, those variables that were statistically significant at the 0.05 level were included in the final model. All variables were considered independent variables for the outcome variable.
Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Ethics Committee of the Atlas College of Health Sciences (Ref. No: ACHS/001/22). A letter of support was provided to the Nash Specialty Dental Clinic, the Sitamin Medium Dental Clinic, the Dent-Efrata Medium Dental Clinic, and the Merit Medium Dental Clinic. Participants were informed of the purpose of the study, and informed consent was obtained before the study began. Once permission was obtained to conduct the study, each ethical procedure was strictly followed throughout the study.
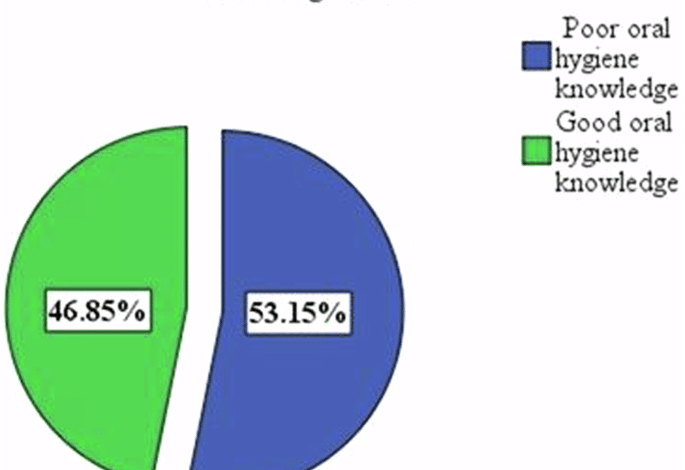
Good knowledge
Participants who knew that dental plaque and calculus were harmful believed that they would maintain oral health through brushing, using dental floss, and performing regular dental check-ups for professional cleaning; scores ranged from 7 to 9 for 9 questions about oral hygiene knowledge [20].
Poor knowledge
A participant who is unaware that dental plaque and calculus are harmful and who does not believe in maintaining oral health through brushing, using dental floss, or performing regular dental check-ups for professional cleaning scores 0 to 6 on 9- knowledge questions [20].
Good oral hygiene practices
Participants who brushed their teeth twice or more a day, cleaned their tongue and interdental spaces, changed their brush every 3 months, and had regular professional cleaning scores of 5 to 8 from eight oral hygiene practice questions [13].
Poor oral hygiene practice
Participants who sometimes cleaned their teeth, never changed their brush regularly, never had professional cleaning, and never cleaned their teeth scored 0 to 4 on 8 oral hygiene practice questions [13].





